DOWNSTREAM RISK MANAGEMENT
Compliance Support
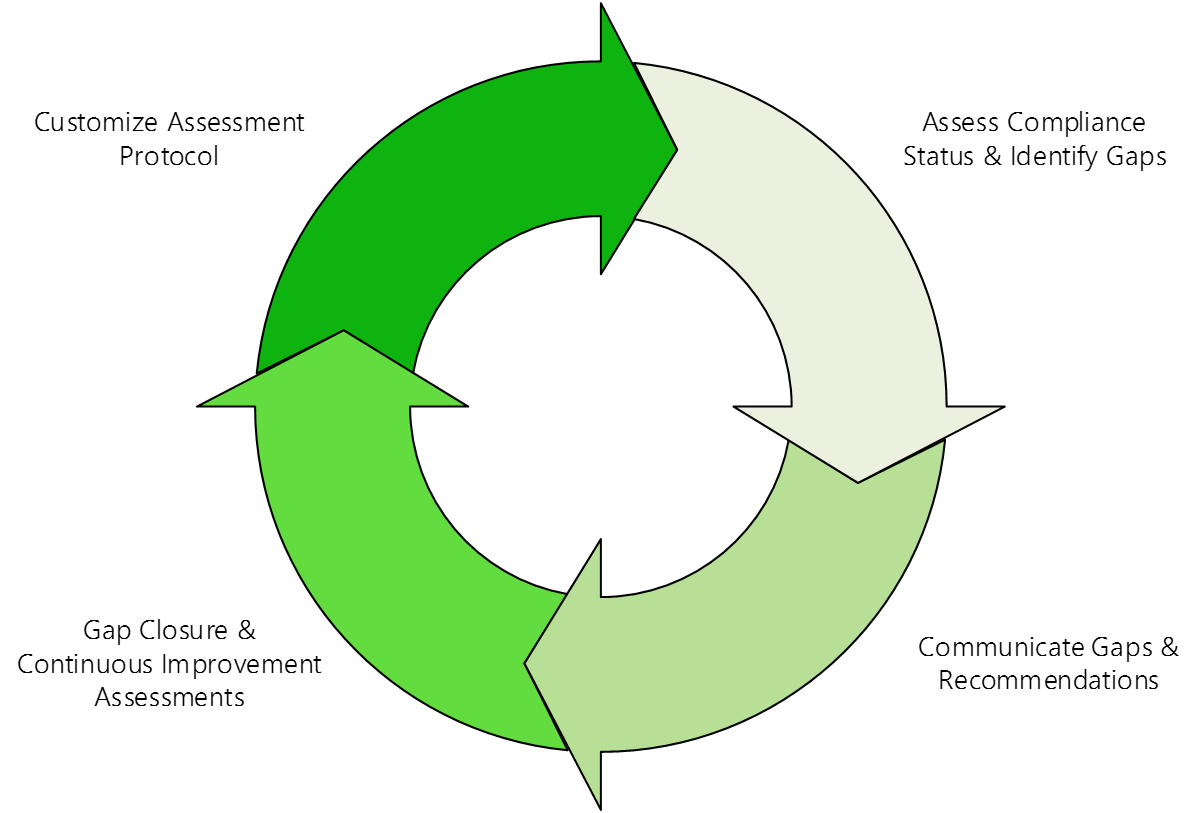
In alignment with existing government and industry regulations, and as new and more stringent standards are approved, Energy Risk Consulting can provide support to assess compliance status with requirements, and to develop and implement strategies to close identified gaps.
ERC can support organizations to achieve comprehensive compliance with:
Government Regulations and Requirements
Industry Standards and Requirements (API, ISO, etc.)
Internal Company Policies and Governance
Process
Comprehensive and Detailed: Our assessment process is directly aligned with the applicable regulations and standards and provides for a thorough evaluation and understanding of compliance status.
Organized and Repeatable: A structured project execution approach is applied for each assessment to ensure clear alignment on expectations and complete documentation of the process and results.
Collaborative: ERC works closely and collaboratively with clients to define assessment needs and customize the implementation approach to achieve customer objectives.

OSHA 1910.119 – Process Safety Management
Unexpected releases of toxic, reactive, or flammable liquids and gases in processes involving highly hazardous chemicals have been reported for many years in various industries that use chemicals with such properties. Regardless of the industry that uses these highly hazardous chemicals, there is a potential for an accidental release any time they are not properly controlled, creating the possibility of disaster.
To help ensure safe and healthful workplaces, OSHA has issued the Process Safety Management (PSM) of Highly Hazardous Chemicals standard (29 CFR 1910.119), which contains requirements for the management of hazards associated with processes using highly hazardous chemicals. OSHA’s standard emphasizes the management of hazards associated with highly hazardous chemicals and establishes a comprehensive management program that integrates technologies, procedures, and management practices. Key elements of the PSM standard and areas where Energy Risk Consulting can provide support to clarify requirements and develop and implement strategies to achieve compliance.
Knowledge Management
Successful and sustainable management of knowledge and information is critical to the success of every organization. The OSHA Process Safety Management (PSM) of highly hazardous chemicals standard (29 CFR 1910.119) requires that all applicable facilities retain and manage a significant volume of operational, technical, and organizational information. The intent of retaining and making the appropriate information available to employees directly supports preventing or minimizing the consequences of catastrophic releases of toxic, reactive, flammable, or explosive chemicals which may result in toxic, fire, or explosion hazards.
Management of the large volume of information required to support this requirement can be a challenge for any organization, particularly those with large and complex facilities. Developing a practical and sustainable methodology for consistently managing controlled information across an organization, therefore, is critical to protecting the safety of employees and the environment, and to preventing or minimizing financial losses due to missing or inaccurate information.
Energy Risk Consulting (ERC) employees have extensive experience supporting development of sustainable systems to manage knowledge and information at facilities.
Understanding that a single solution cannot be generically applied to any facility, ERC’s approach to developing knowledge management solutions for an organization is based on leveraging previous experience and on three core principles of a successful knowledge management system.
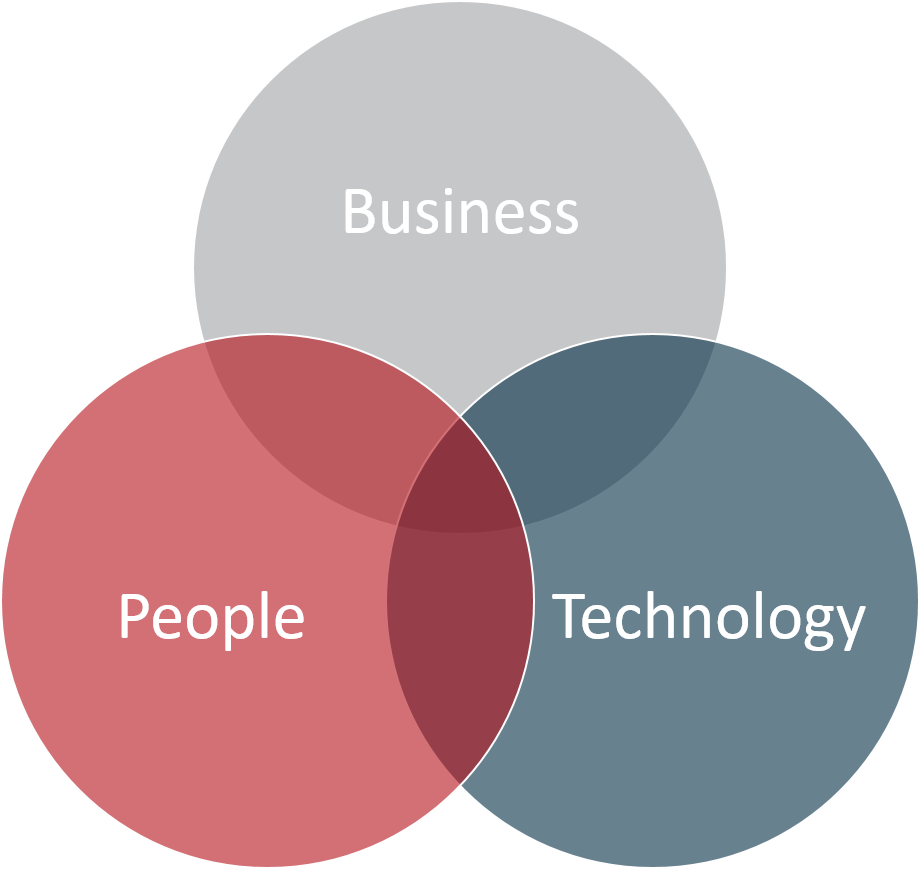
Business
Clear definition of business/functional requirements and scope of information to be managed based on a facility’s organizational structure, work processes, and system interactions
Development of documented policies, procedures, work processes, and governance to ensure sustainability
Definition of key performance indicators and metrics to measure continued compliance with the system and to pro-actively identify concerns and instances of non-compliance
People
Development of employee training initiatives. In many instances, a paradigm shift in culture is necessary to ensure that a knowledge management system is successful.
Engaging management to support the developed system and providing employees with appropriate and adequate training is essential to clearly communicate information ownership and accountabilities, change management strategies, and information taxonomies.
Technology
Development of a clear technology selection process to understand potential system deficiencies and limitations, to ensure that the selected technology solutions align with business/functional requirements
Completion of thorough testing to ensure that the selected system is functional and free of errors when delivered
Development of a lifecycle process to address management of future upgrades/updates, system stability and maintenance, user rights, and business continuity and disaster recovery processes and systems
Risk Analysis
With global experience conducting risk analyses on an extensive number of technical systems for a variety of customers, Energy Risk Consulting is committed to supporting clients in minimizing risks to safety, the environment, and operations. Our ability to utilize a wide variety of risk analysis methodologies (including HAZID, HAZOP, LOPA, FMECA, etc.), coupled with our streamlined work process, allows us to develop unique solutions for each customer which maximize value while minimizing cost and session duration.
Benefits
Identification of critical risks with potential for safety, environmental, and business impacts
Increased understanding of systems and interfaces via system overview discussions and detailed analyses
Development of recommendations (including SIT) to mitigate risks, increase system reliability and safety, and decrease downtime
Methodology
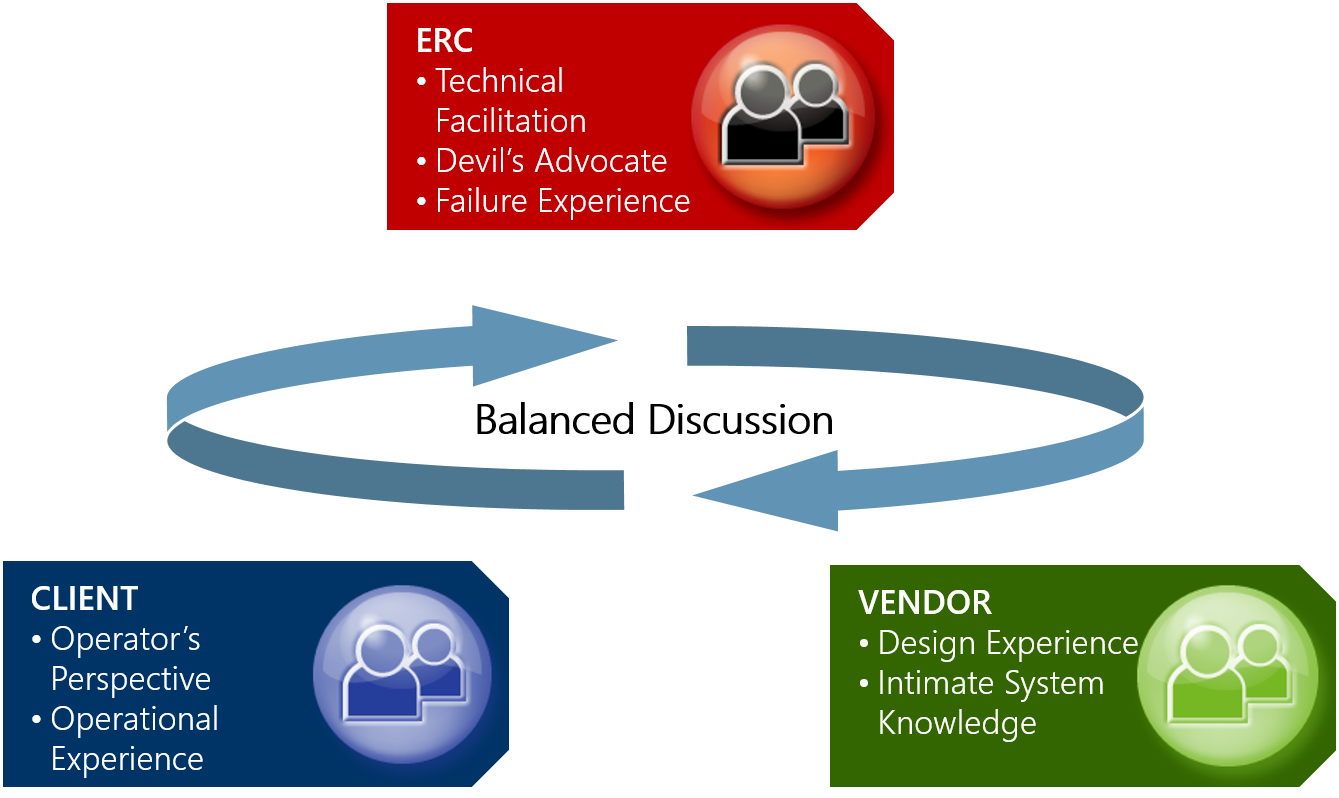
Energy Risk Consulting is focused on maximizing value and productivity during hazards analysis sessions/meetings. The standard approach for conducting these meetings is to begin each review with blank documentation and utilize a brainstorming approach coupled with the selected methodology (HAZID, HAZOP, FMEA/FMECA, etc.) to identify scenarios and populate the associated worksheets. Although our experienced staff are fully capable of using this approach, in the interest of maximizing the value of the review sessions where a number of participants from the customer (project, engineering, and operations staff) and vendor(s) may be involved, alternative strategies may be used.

With a risk management staff consisting of experienced engineers, Energy Risk Consulting is capable of reviewing technical system documentation (Electrical Diagrams, Hydraulic System Diagrams, P&IDs, etc.) to develop preliminary system failure scenarios (failure causes and modes only – consequences and risk ranking are always recommended to be completed during sessions). In addition, our recommended approach involves scheduling a brief preliminary meeting, or preparation session, with a small group of engineering staff knowledgeable of the system design. The intent of this preparation session is to:
Verify the scope of the suggested study nodes
Verify the accuracy of preliminary system failure scenarios
Establish and build relationships with the meeting participants which increases productivity during the full hazards analysis sessions
Using this work process to prepare for and execute hazards analysis meetings increases session productivity and value in the following ways:
Minimizes session duration – preliminary preparation by Energy Risk Consulting engineering professionals coupled with the preparation session with the small group of design engineers allows for the majority of failure scenarios to be identified and pre-populated into worksheets prior to starting the formal hazards analysis meetings. This preparation work, therefore, eliminates the time that would have been spent developing and documenting these scenarios during a formal session with the full group of participants, significantly reducing both the session duration and cost.
Allows participants to focus creative brainstorming on identifying less obvious system failures – an additional benefit of preparing failure scenarios and documentation prior to the hazards analysis sessions is that participants are then able to focus discussions on the consequences and risks of the identified failures, and on creative brainstorming of additional failure scenarios that are less obvious, such as those that are based on operational experience.
Session Approach